A couple of years ago when poet and former head of the NEA, Dana Gioia, came to Messiah College to speak to our faculty and the honors program, I asked him if he felt there were connections between his work as a poet and his other careers as a high-level government administrator and business executive. Gioia hemmed and hawed a bit, but finally said no; he thought he was probably working out of two different sides of his brain.
 I admit to thinking the answer was a little uncreative for so creative a person. I’ve always been a bit bemused by and interested in the various connections that I make between the different parts of myself. Although I’m not a major poet like Gioia, I did complete an MFA and continue to think of myself in one way or another as a writer, regardless of what job I happen to be doing at the time. And I actually think working on an MFA for those two years back in Montana has had a positive effect on my life as an academic and my life as an administrator. Some day I plan to write an essay on the specifics, but it is partially related to the notion that my MFA did something to cultivate my creativity, to use the title of a very good article in the Chronicle review by Steven Tepper and George Kuh. According to Tepper and Kuh,
I admit to thinking the answer was a little uncreative for so creative a person. I’ve always been a bit bemused by and interested in the various connections that I make between the different parts of myself. Although I’m not a major poet like Gioia, I did complete an MFA and continue to think of myself in one way or another as a writer, regardless of what job I happen to be doing at the time. And I actually think working on an MFA for those two years back in Montana has had a positive effect on my life as an academic and my life as an administrator. Some day I plan to write an essay on the specifics, but it is partially related to the notion that my MFA did something to cultivate my creativity, to use the title of a very good article in the Chronicle review by Steven Tepper and George Kuh. According to Tepper and Kuh,
To fuel the 21st-century economic engine and sustain democratic values, we must unleash and nurture the creative impulse that exists within every one of us, or so say experts like Richard Florida, Ken Robinson, Daniel Pink, Keith Sawyer, and Tom Friedman. Indeed, just as the advantages the United States enjoyed in the past were based in large part on scientific and engineering advances, today it is cognitive flexibility, inventiveness, design thinking, and nonroutine approaches to messy problems that are essential to adapt to rapidly changing and unpredictable global forces; to create new markets; to take risks and start new enterprises; and to produce compelling forms of media, entertainment, and design.
Tepper and Kuh , a sociologist and professor education respectively, argue forcefully that creativity is not doled out by the forces of divine or genetic fate, but something that can be learned through hard work. An idea supported by recent findings that what musical and other artistic prodigies share is not so much genetic markers as practice, according to Malcolm Gladwell 10,000 hours of it. Tepper and Kuh believe the kinds of practice and discipline necessary for cultivating a creative mindset are deeply present in the arts, but only marginally present in many other popular disciplines on campus.
Granted, other fields, like science and engineering, can nurture creativity. That is one reason collaborations among artists, scientists, and engineers spark the powerful breakthroughs described by the Harvard professor David Edwards (author of Artscience, Harvard University Press, 2008); Xerox’s former chief scientist, John Seely Brown; and the physiologist Robert Root-Bernstein. It is also the case that not all arts schools fully embrace the creative process. In fact, some are so focused on teaching mastery and artistic conventions that they are far from hotbeds of creativity. Even so, the arts might have a special claim to nurturing creativity.
A recent national study conducted by the Curb Center at Vanderbilt University, with Teagle Foundation support, found that arts majors integrate and use core creative abilities more often and more consistently than do students in almost all other fields of study. For example, 53 percent of arts majors say that ambiguity is a routine part of their coursework, as assignments can be taken in multiple directions. Only 9 percent of biology majors say that, 13 percent of economics and business majors, 10 percent of engineering majors, and 7 percent of physical-science majors. Four-fifths of artists say that expressing creativity is typically required in their courses, compared with only 3 percent of biology majors, 16 percent of economics and business majors, 13 percent of engineers, and 10 percent of physical-science majors. And arts majors show comparative advantages over other majors on additional creativity skills—reporting that they are much more likely to have to make connections across different courses and reading; more likely to deploy their curiosity and imagination; more likely to say their coursework provides multiple ways of looking at a problem; and more likely to say that courses require risk taking.
Tepper and Kuh focus on the arts for their own purposes, and I realized that in thinking about the ways that an MFA had helped me I was thinking about an arts discipline in many respects. However, the fact that the humanities is nowhere in their article set me to thinking. How do the humanities stack up in cultivating creativity, and is this a selling point for parents and prospective students to consider as they imagine what their kids should study in college. These are my reflections on the seven major “creative” qualities that Kepper and Kuh believe we should cultivate, and how the humanities might do in each of them.
- the ability to approach problems in nonroutine ways using analogy and metaphor;
- I think the humanities excel in this area for a variety of reasons. For some disciplines like English and Modern Languages, we focus on the way language works with analogy and metaphor and we encourage its effective use in writing. But more than that, I think many humanities disciplines can encourage nonroutine ways of approaching problems—though, of course, many professors in any discipline can be devoted to doing the same old things the same old way.
- conditional or abductive reasoning (posing “what if” propositions and reframing problems);
- Again, I think a lot of our humanities disciplines approach things in this fashion. To some degree this is because of a focus on narrative. One way of getting at how narrative works and understanding the meaning of a narrative at hand is to pose alternative scenarios. What if we had not dropped the bomb on Japan? What if Lincoln had not been shot? How would different philosophical assumptions lead to different outcomes to an ethical problem.
- keen observation and the ability to see new and unexpected patterns;
- I think we especially excel in this area. Most humanities disciplines are deeply devoted to close and careful readings that discover patterns that are beneath the surface. The patterns of imagery in a poem, the connections between statecraft and everyday life, the relationship between dialogue and music in a film. And so forth. Recognizing patterns in problems can lead to novel and inventive solutions.
- the ability to risk failure by taking initiative in the face of ambiguity and uncertainty;
- I’m not sure if the humanities put a premium on this inherently or not. I know a lot of professors (or at least I as a professor) prefer their students take a risk in doing something different on a project and have it not quite work than to do the predictable thing. But I don’t know that this is something inherent to our discipline. I do think, however, that our disciplines inculcate a high level of comfort with uncertainty and ambiguity. Readings of novels or the complexities of history require us to not go for easy solutions but to recognize and work within the ambiguity of situations.
- the ability to heed critical feedback to revise and improve an idea;
- Again, I would call this a signature strength, especially as it manifests itself in writing in our discipline and in the back and forth exchange between students and student and teacher. Being willing to risk and idea or an explanation, have it critiqued, and then to revise one’s thinking in response to more persuasive arguments.
- a capacity to bring people, power, and resources together to implement novel ideas; and
- I admit that on this one I kind of think the humanities might be weaker than we should be, at least as manifested in our traditional way of doing things. Humanists in most of our disciplines are notorious individualists who would rather spend their time in libraries. We don’t get much practice at gathering people together with the necessary resources to work collaboratively. This can happen, but instinctively humanists often want to be left alone. This is an area where I think a new attention to collaborative and project based learning could help the humanities a great deal, something we could learn from our colleagues in the sciences and arts like theatre and music. I’m hopeful that some of the new attention we are giving to digital humanities at Messiah College will lead us in this direction.
- the expressive agility required to draw on multiple means (visual, oral, written, media-related) to communicate novel ideas to others.
- A partial strength. I do think we inculcate good expressive abilities in written and moral communication, and we value novel ideas. Except for our folks in film and communication—as well as our cousins in art history—we are less good at working imaginatively with visual and other media related resources. This has been one of my priorities as dean, but something that’s hard to generate from the ground up.
Well, that’s my take. I wonder what others think?










 As my colleague, Matt Roth, suggests it’s hard to know which is worse, that they made the bed in the first place, or that they didn’t know about
As my colleague, Matt Roth, suggests it’s hard to know which is worse, that they made the bed in the first place, or that they didn’t know about  temple reader and the town crier are the original of audiobooks and podcasts. In ancient Palestine, for instance,
temple reader and the town crier are the original of audiobooks and podcasts. In ancient Palestine, for instance, 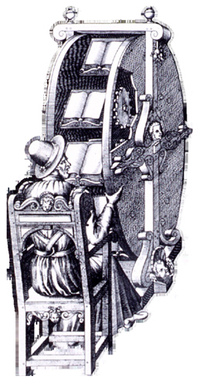 of them at the same time. This is not exactly the same thing as multi-tasking that Scott abhors in his post, and it’s not exactly internet hypertexting, but it is clearly not the singular absorption in a text that we’ve come to associate with the word “reading.” “Reading” is not just the all-encompassing absorption that I’ve come to treasure and long for in great novels and poems, or even in great and well-written arguments. Indeed, I judge books by whether they can provide this kind of experience. Nevertheless, “Reading” is many things.
of them at the same time. This is not exactly the same thing as multi-tasking that Scott abhors in his post, and it’s not exactly internet hypertexting, but it is clearly not the singular absorption in a text that we’ve come to associate with the word “reading.” “Reading” is not just the all-encompassing absorption that I’ve come to treasure and long for in great novels and poems, or even in great and well-written arguments. Indeed, I judge books by whether they can provide this kind of experience. Nevertheless, “Reading” is many things.